Prove and claim carbon capture
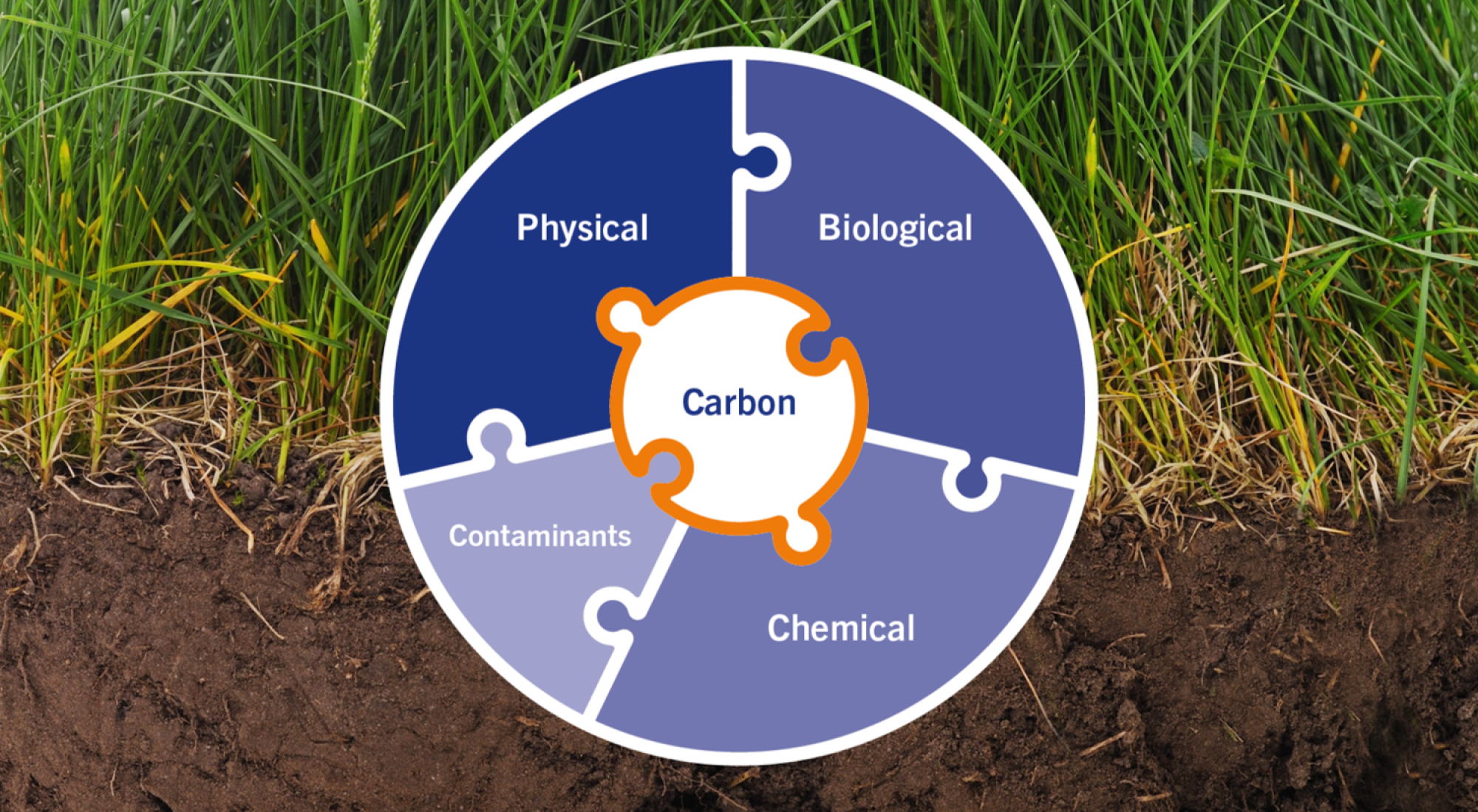
Soil organic carbon is often considered as the most important element of soil health because of its effect on physical (e.g. soil workability, water holding capacity, root penetrability), chemical (e.g. K-, Ca-, Mg-binding capacity) and biological (e.g. soil biodiversity, soil workability, disease suppression, N and S mineralization) components of soil health. Soil Carbon Check makes it possible to prove and claim sustainability in the agri-food chain. Various systems are being developed to reward farmers for their efforts to capture CO2.